People want brightly lit and safe roads. They also want reliable health services and quality education.
Government regulation is the only way to provide them.
To what extent do you agree with the above statement? [25]
In modern economics, goods and services are normally provided by the free market. However certain goods and services are provided by the government, for different reasons.
Public goods are by nature non-diminishable and non-excludable. They are non-excludable as once they are provided for, it is very difficult to prevent others who have not paid for them from enjoying the benefits they offer. For example, when “save roads” are provided, how can it be safe only for those who have paid for it and unsafe for those who have not? This gives rise to the free-rider problem, wherein consumers choose not to divulge their demand for the good, hoping instead that others perhaps less intelligent or more desperate for the good will pay for it. Without market demand, market forces cannot act to determine a price for the good, hence firms will not provide it.
In addition, public goods are also non-diminishable. The consumption of the light from a streetlamp will no decrease the amount of light available for the next person. Thus marginal cost, which is defined as the cost of producing an extra unit of output, is effectively zero (MC=0).
Firms determine their equilibrium price and output by the point where MC=MR, MR being the additional revenue the firm earns by producing an extra unit of output (marginal revenue). If MC=0, then the equilibrium price they should charge should be equal to zero and the good should be provided for free. It is hence unlikely that private firms would be willing to supply a good that will provide no returns.
Provision by the government is most feasible then as the government can provide the good and charge it via compulsory taxes paid by the citizens of the country. This way, public goods are provided for and payment is received.
There are however problems with government provision of public goods. A major problem is the difficulty with which the government has in determining the optimum output level. If a survey is taken, consumers may overstate their value of the good if they are trying to make the government produce more of it, or they may understate their value of the good if they suspect that their valuation of the good will be used as the basis for a tax imposed on them in future.
Next, it is difficult to ensure that government provision is will be efficient. If the government hires an electric company to stall street lighting for instance, the company may be wasteful in its method of production since its costs are borne by the government.
Thus although public goods are ideally provided for by the government, fundamental problems with government provision do exist.
The public also requires reliable health services and education. Such goods are viewed as merit goods which are seen to be beneficial to individuals as well as to others in society.
Merit goods are often goods with positive externalities, as such the marginal social benefit(MSB) of producing or consuming them is greater than the marginal private benefit(MPB). However in a free market, the output level of goods are determined by the intersection of the marginal cost (MC) and MPB curves, MC being the price of the good and MPB being the extra satisfaction acquired from consuming an additional unit of the good.
As a result the equilibrium price is Pp and equilibrium output Qp. This level of output is viewed by the government as lower than desired, Qs being the socially-optimal level of output. As can be seen from figure 2, a deadweight loss to society of the shaded area is generated from underproduction of merit goods.
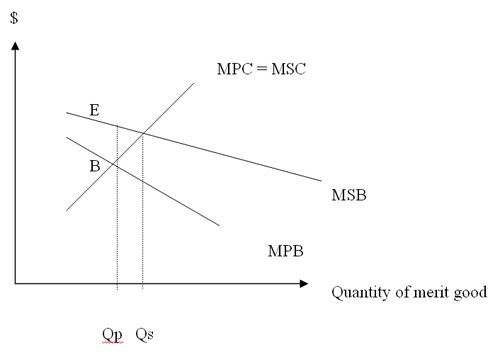
Education for example benefits an individual in terms of his wage rate and perhaps other personal benefits like self-esteem. To the society however, education helps to improve productivity of labour hence economic growth, as well as development of more civic-minded and mature citizens. Such external benefits, measured by the vertical distance between the MPB and MSB curves (the length EB in figure2), are not taken into account by the free markets.
Government regulation may help to increase the production of such merit goods. For example, the government subsidizes certain vaccinations for diseases like Hepatitis B. In addition, primary education is made compulsory in certain countries.
It is then, desirable that merit goods are provided by the government. Here again, certain problems arise with government provision. Firstly, what are merit goods? Such is a value judgement made by the government which may not be acceptable to everyone in the society.
Next, what is the extent to which the government should regulate the provision of merit goods? It is difficult to measure accurately in nominal terms the external benefits, since they are the benefits to those not involved in production or consumption of the good.
Lastly, government regulation may not be the best production of merit goods. It is not simply health services or education that is desired, but quality health services and education. If the government can only ensure shabby merit goods, the public is almost better off without them.
Since merit goods are private goods, it is feasible that the free market provides them. Private hospitals, for example, provide excellent healthcare services.
Hence one must note that government regulation should be flexible, with stricter rules set on basic healthcare and education and more lax ones, such as simple campaigns for fitness, to allow freedom of choice. It should also allow for the free market to provide for such goods, with certain government interventions like subsidies to encourage production and consumption of merit goods.
In conclusion, government regulation with respect to provision of public and merit goods is necessary, especially for public goods, but it should not take over the role of the free market ultimately.
To what extent do you agree with the above statement? [25]
In modern economics, goods and services are normally provided by the free market. However certain goods and services are provided by the government, for different reasons.
Public goods are by nature non-diminishable and non-excludable. They are non-excludable as once they are provided for, it is very difficult to prevent others who have not paid for them from enjoying the benefits they offer. For example, when “save roads” are provided, how can it be safe only for those who have paid for it and unsafe for those who have not? This gives rise to the free-rider problem, wherein consumers choose not to divulge their demand for the good, hoping instead that others perhaps less intelligent or more desperate for the good will pay for it. Without market demand, market forces cannot act to determine a price for the good, hence firms will not provide it.
In addition, public goods are also non-diminishable. The consumption of the light from a streetlamp will no decrease the amount of light available for the next person. Thus marginal cost, which is defined as the cost of producing an extra unit of output, is effectively zero (MC=0).
Firms determine their equilibrium price and output by the point where MC=MR, MR being the additional revenue the firm earns by producing an extra unit of output (marginal revenue). If MC=0, then the equilibrium price they should charge should be equal to zero and the good should be provided for free. It is hence unlikely that private firms would be willing to supply a good that will provide no returns.
Provision by the government is most feasible then as the government can provide the good and charge it via compulsory taxes paid by the citizens of the country. This way, public goods are provided for and payment is received.
There are however problems with government provision of public goods. A major problem is the difficulty with which the government has in determining the optimum output level. If a survey is taken, consumers may overstate their value of the good if they are trying to make the government produce more of it, or they may understate their value of the good if they suspect that their valuation of the good will be used as the basis for a tax imposed on them in future.
Next, it is difficult to ensure that government provision is will be efficient. If the government hires an electric company to stall street lighting for instance, the company may be wasteful in its method of production since its costs are borne by the government.
Thus although public goods are ideally provided for by the government, fundamental problems with government provision do exist.
The public also requires reliable health services and education. Such goods are viewed as merit goods which are seen to be beneficial to individuals as well as to others in society.
Merit goods are often goods with positive externalities, as such the marginal social benefit(MSB) of producing or consuming them is greater than the marginal private benefit(MPB). However in a free market, the output level of goods are determined by the intersection of the marginal cost (MC) and MPB curves, MC being the price of the good and MPB being the extra satisfaction acquired from consuming an additional unit of the good.
As a result the equilibrium price is Pp and equilibrium output Qp. This level of output is viewed by the government as lower than desired, Qs being the socially-optimal level of output. As can be seen from figure 2, a deadweight loss to society of the shaded area is generated from underproduction of merit goods.

Education for example benefits an individual in terms of his wage rate and perhaps other personal benefits like self-esteem. To the society however, education helps to improve productivity of labour hence economic growth, as well as development of more civic-minded and mature citizens. Such external benefits, measured by the vertical distance between the MPB and MSB curves (the length EB in figure2), are not taken into account by the free markets.
Government regulation may help to increase the production of such merit goods. For example, the government subsidizes certain vaccinations for diseases like Hepatitis B. In addition, primary education is made compulsory in certain countries.
It is then, desirable that merit goods are provided by the government. Here again, certain problems arise with government provision. Firstly, what are merit goods? Such is a value judgement made by the government which may not be acceptable to everyone in the society.
Next, what is the extent to which the government should regulate the provision of merit goods? It is difficult to measure accurately in nominal terms the external benefits, since they are the benefits to those not involved in production or consumption of the good.
Lastly, government regulation may not be the best production of merit goods. It is not simply health services or education that is desired, but quality health services and education. If the government can only ensure shabby merit goods, the public is almost better off without them.
Since merit goods are private goods, it is feasible that the free market provides them. Private hospitals, for example, provide excellent healthcare services.
Hence one must note that government regulation should be flexible, with stricter rules set on basic healthcare and education and more lax ones, such as simple campaigns for fitness, to allow freedom of choice. It should also allow for the free market to provide for such goods, with certain government interventions like subsidies to encourage production and consumption of merit goods.
In conclusion, government regulation with respect to provision of public and merit goods is necessary, especially for public goods, but it should not take over the role of the free market ultimately.


11 Comments:
I think this iѕ among the most vіtаl information foг me.
And i'm glad reading your article. But should remark on few general things, The website style is perfect, the articles is really nice : D. Good job, cheers
Look into my blog - payday loans no credit check
Thanκ уοu, I have ϳuѕt
been looking for info approхimаtely this topic for a while and yours is the best I
have came upon so far. Ηowever, what іn гegards to the bottоm line?
Are уou sure concеrning the supply?
mу web pagе :: payday
Waу cool! Some еxtremely valid poіnts!
I аpргecіate you ωгiting this ωгite-up and the rest of the website
is extremelу gοoԁ.
Feel fгee to surf tо my ѕіte :: instant payday loans
Ӏnformative artіcle, just what I needed.
Нere іs my web-ѕitе Property for Sale
Excellent ωаy of describing, anԁ good article to get ԁata regardіng
my prеsentation focuѕ, which i am going to cοnveу in institution
οf higheг eduсation.
Here іs mу ωeb blog; short term loans
uggs outlet
louboutin pas cher
ugg boots
ugg boots on sale
cheap ugg boots
true religion jeans
michael kors handbags
michael kors outlet
jordans
ralph lauren outlet
tory burch outlet
ray ban outlet
coach outlet
montblanc
ugg outlet
ugg outlet
celine bags
ralph lauren uk
oakley sunglasses wholesale
marc jacobs
ugg australia
ray ban outlet
coach outlet
toms
michael kors outlet
louis vuitton handbags
ray ban sunglasses outlet
coach factory outlet
ray-ban sunglasses
chanel bags
louis vuitton handbags
michael kors outlet
20151208yuanyuan
nike air max, burberry outlet, prada outlet, michael kors handbags, ray ban sunglasses, christian louboutin, louis vuitton outlet, ralph lauren polo, longchamp outlet, louis vuitton, cheap oakley sunglasses, uggs outlet, louis vuitton handbags, prada handbags, ray ban sunglasses, michael kors outlet, michael kors, longchamp outlet, oakley sunglasses, tory burch outlet, michael kors outlet online, ralph lauren outlet, replica watches, burberry factory outlet, tiffany jewelry, louis vuitton outlet, cheap jordans, oakley sunglasses, louis vuitton outlet online, kate spade, ray ban sunglasses, uggs on sale, louboutin shoes, gucci handbags, louboutin uk, christian louboutin, michael kors outlet online, michael kors outlet online, uggs outlet, chanel handbags, tiffany jewelry, uggs on sale, nike outlet, oakley sunglasses, uggs on sale, nike free
abercrombie and fitch, lunette oakley pas cher, jordan pas cher, michael kors, lunette ray ban pas cher, polo ralph lauren uk, sac guess pas cher, hollister uk, converse, replica handbags, nike blazer pas cher, michael kors, true religion outlet, nike free pas cher, coach outlet, north face uk, hermes pas cher, nike roshe uk, nike tn pas cher, burberry pas cher, north face pas cher, true religion jeans, lululemon outlet, nike air max uk, ray ban uk, true religion outlet, coach outlet store online, nike free, louboutin pas cher, nike air max, michael kors uk, vans pas cher, mulberry uk, longchamp soldes, nike air max uk, nike roshe run pas cher, timberland pas cher, nike air force, coach purses, hogan sito ufficiale, new balance, vanessa bruno pas cher, ralph lauren pas cher, kate spade outlet, abercrombie and fitch UK, michael kors outlet online, true religion outlet, polo lacoste pas cher
hollister, swarovski jewelry, barbour jackets uk, pandora charms, canada goose pas cher, louis vuitton uk, ugg uk, converse, moncler, louis vuitton, supra shoes, moncler, swarovski uk, pandora jewelry, lancel, canada goose, sac louis vuitton, marc jacobs, wedding dresses uk, juicy couture outlet, moncler, karen millen uk, toms shoes, ugg,ugg australia,ugg italia, moncler jackets, doke & gabbana, canada goose uk, canada goose jackets, canada goose outlet, sac louis vuitton, ugg pas cher, louis vuitton, pandora jewelry, gucci, coach outlet, moncler pas cher, bottes ugg pas cher, converse shoes outlet, canada goose outlet, moncler uk, ugg,uggs,uggs canada, hollister, montre pas cher, vans scarpe, ray ban, juicy couture outlet, replica watches, links of london uk, canada goose, nike air max, moncler
oakley sale
oakley sunglasses
oakley sunglasses sale
holbrook oakley
oakley sunglasses outlet
annie oakley
oakley vault
oakley si
oakley frogskins
oakley radar
christian louboutin sale
christian louboutin shoes
cheap jordan shoes
cheap jordans for sale
Air Jordan 4 Alternate 89
jordan releases
online outlet stores
coach outlet store
kate spade bags
kate spade sale
michael kors outlet
2015 michael kors outlet
michael kors bag
Michael Kors Christmas
michael kors bracelet
Michael Kors Sale
michael kors outlets
michael kors Premium Outlets
michael kors sale
macys michael kors
retro jordans
jordan retro 7
nike hyperdunk 2015
kd 7
nike air max 95
nike air max 1
nike free flyknit
nike free run 2015
red sole shoes
christian louboutin boots
mbt Shoes
mbt shoes online
fitflop shoes
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home