Do you think monetary policy alone is sufficient to achieve a low rate of inflation? (25)
Monetary policy (MP) is the policy that involves the control of money supply (MS) that will affect interest rates, thus affecting the level of investment and affecting aggregate expenditure (AE), which eventually affects the equilibrium income of the economy. This chain effect can be illustrated using the diagrams below.
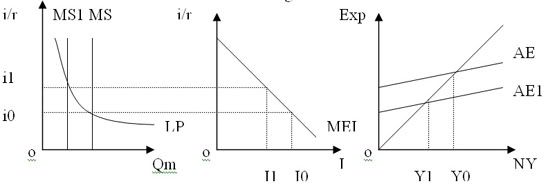
The central bank decreases MS from MS to MS1 thus increasing the interest rates from oi0 to oi1. With the increase in interest rates, the level of investment (I) reduces from oI0 to oI1 and this decrease in I lowers AE and if the economy is at full employment at oY1, then the decrease in AE will close the inflationary gap.
However, the MP works only assuming that the demand for money is inelastic and investment is interest elastic. If the demand for money is elastic, the decrease in MS will only lead to a small increase in interest rates that may be too small to affect investment and eventually the equilibrium NY of the economy. Moreover, if investment is interest inelastic, an increase in interest rates will not lead to a substantial decrease in the level of investment, thus not able to affect AE.
An increase in interest rates may also help reduce households’ consumption (C) because if interest rates are too high, consumers may not want to borrow to spend, as they would have to pay back even more. However, this would not be a problem if consumption were dependent on disposable income (Yd) rather than interest rates. Hence MP alone is not sufficient to achieve low rate of inflation and there are other policies like fiscal policy (FP), which can help achieve a low rate of inflation.
FP is the measure taken by the government to either increase or decrease AE and to lower inflation rates, contractionary policy is used. Contractionary FP would include either increasing taxes (T) or decreasing government spending (G).
By increasing T, the amount of Yd of households is lowered and thus they will decrease C, which will lead to a decrease in AE and a decrease in equilibrium NY through the multiplier.
Decreasing G has the same effect as T. Between increasing T and decreasing G, decreasing G would be a more certain policy of the 2 because an increase in T may not necessarily lead to a fall in C especially if consumers are no affected by tax increases. Decreasing G may decrease AE more effectively than decreasing MS given the uncertain impact on interest rates and I.
The increase in interest rates, decreasing G and increasing T are policies that will only work if the inflation is one that is a demand-pull inflation. Since these policies are followed by unemployment and a cost-push inflation is also followed by a recession, these policies will only worsen the recession and hence inappropriate for cost-push inflation.
Cost-push inflation occurs when there is an increase in the cost of production e.g. unions asking for higher wages for their workers, increase in the price of raw materials, which will increase the average total cost of the firm.
This kind of inflation would require supply side policies to lower the inflation rate. Short-term supply side policies include wage-price controls where wage and price increases may be frozen or capped. However, such policies are difficult to implement because it would require the firm to earn less profits, which not many are willing. In addition, there is a huge cost in implementing and monitoring the controls. The controls also lead to misallocation of resources.
Therefore long-term supply side policies are a much better way in lowering inflation caused by cost-push. These policies include increasing education and skills training that will in turn increase the productivity of the workers, which equate to larger output. Long-term supply side policies potentially shift out the production possibility curve, which is what the economy wants to achieve. Another long-term policy would be to encourage investment in the country. This can be done through the government giving tax incentives so that more firms will be willing to invest. Investment in the long term would lead to increase in output thus increasing NY.
MP may be a way to achieve low rates of inflation but it is not the only way as there is also FP in the form of decreasing G that can achieve the same effects but more certain impact. The type of inflation should be in mind also because MP and FP only works if inflation is demand-pull inflation and solutions to cost-push inflation would require long term supply side policies.

The central bank decreases MS from MS to MS1 thus increasing the interest rates from oi0 to oi1. With the increase in interest rates, the level of investment (I) reduces from oI0 to oI1 and this decrease in I lowers AE and if the economy is at full employment at oY1, then the decrease in AE will close the inflationary gap.
However, the MP works only assuming that the demand for money is inelastic and investment is interest elastic. If the demand for money is elastic, the decrease in MS will only lead to a small increase in interest rates that may be too small to affect investment and eventually the equilibrium NY of the economy. Moreover, if investment is interest inelastic, an increase in interest rates will not lead to a substantial decrease in the level of investment, thus not able to affect AE.
An increase in interest rates may also help reduce households’ consumption (C) because if interest rates are too high, consumers may not want to borrow to spend, as they would have to pay back even more. However, this would not be a problem if consumption were dependent on disposable income (Yd) rather than interest rates. Hence MP alone is not sufficient to achieve low rate of inflation and there are other policies like fiscal policy (FP), which can help achieve a low rate of inflation.
FP is the measure taken by the government to either increase or decrease AE and to lower inflation rates, contractionary policy is used. Contractionary FP would include either increasing taxes (T) or decreasing government spending (G).
By increasing T, the amount of Yd of households is lowered and thus they will decrease C, which will lead to a decrease in AE and a decrease in equilibrium NY through the multiplier.
Decreasing G has the same effect as T. Between increasing T and decreasing G, decreasing G would be a more certain policy of the 2 because an increase in T may not necessarily lead to a fall in C especially if consumers are no affected by tax increases. Decreasing G may decrease AE more effectively than decreasing MS given the uncertain impact on interest rates and I.
The increase in interest rates, decreasing G and increasing T are policies that will only work if the inflation is one that is a demand-pull inflation. Since these policies are followed by unemployment and a cost-push inflation is also followed by a recession, these policies will only worsen the recession and hence inappropriate for cost-push inflation.
Cost-push inflation occurs when there is an increase in the cost of production e.g. unions asking for higher wages for their workers, increase in the price of raw materials, which will increase the average total cost of the firm.
This kind of inflation would require supply side policies to lower the inflation rate. Short-term supply side policies include wage-price controls where wage and price increases may be frozen or capped. However, such policies are difficult to implement because it would require the firm to earn less profits, which not many are willing. In addition, there is a huge cost in implementing and monitoring the controls. The controls also lead to misallocation of resources.
Therefore long-term supply side policies are a much better way in lowering inflation caused by cost-push. These policies include increasing education and skills training that will in turn increase the productivity of the workers, which equate to larger output. Long-term supply side policies potentially shift out the production possibility curve, which is what the economy wants to achieve. Another long-term policy would be to encourage investment in the country. This can be done through the government giving tax incentives so that more firms will be willing to invest. Investment in the long term would lead to increase in output thus increasing NY.
MP may be a way to achieve low rates of inflation but it is not the only way as there is also FP in the form of decreasing G that can achieve the same effects but more certain impact. The type of inflation should be in mind also because MP and FP only works if inflation is demand-pull inflation and solutions to cost-push inflation would require long term supply side policies.


2 Comments:
hollister, swarovski jewelry, barbour jackets uk, pandora charms, canada goose pas cher, louis vuitton uk, ugg uk, converse, moncler, louis vuitton, supra shoes, moncler, swarovski uk, pandora jewelry, lancel, canada goose, sac louis vuitton, marc jacobs, wedding dresses uk, juicy couture outlet, moncler, karen millen uk, toms shoes, ugg,ugg australia,ugg italia, moncler jackets, doke & gabbana, canada goose uk, canada goose jackets, canada goose outlet, sac louis vuitton, ugg pas cher, louis vuitton, pandora jewelry, gucci, coach outlet, moncler pas cher, bottes ugg pas cher, converse shoes outlet, canada goose outlet, moncler uk, ugg,uggs,uggs canada, hollister, montre pas cher, vans scarpe, ray ban, juicy couture outlet, replica watches, links of london uk, canada goose, nike air max, moncler
Keep it up
http://www.prokr.net/2016/09/furniture-moving-company-hail.html
http://www.prokr.net/2016/09/furniture-moving-company-hafar-al-batin.html
http://www.prokr.net/2016/09/furniture-moving-company-khamis.html
http://www.prokr.net/2016/09/furniture-moving-company-tabuk.html
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home